|
TG Student Pilot Schedule 2024

ADVERTISEMENT: Please check dates at www.thaiairways.com
The requirements are as follows:

Note: Senior year students who expect to graduate with a Bachelor's Degree by July 31, 2024 can apply. However, the following additional documents are required:
1. Certificate showing date of expected graduation 2. Transcript showing complete grades for the first semester of the senior year 3. Complete graduate transcript 4. Bachelor's Degree certificate

Note: Applicants who failed the Aptitude Test are not allowed to reapply until after a three-year period.
RECEIVING ONLINE APPLICATIONS: Please check dates at www.thaiairways.com
ANNOUNCING APPLICATION SUBMISSION APPOINTMENTS: Please check dates at www.thaiairways.com
RECEIVING APPLICATIONS: Please check dates at www.thaiairways.com

Applicants must provide originals of all documents and one photocopy of each document.

Applicants with fake or fraudulently obtained military service exemption certificates will not be allowed to test.
ANNOUNCING NAMES OF APPLICANTS ELIGIBLE FOR THE BASIC KNOWLEDGE TEST: Please check date at www.thaiairways.com

BASIC KNOWLEDGE TEST (08:00 - 12:30): Sunday, May 26, 2024, Examination Centre, Thammasat University (Rangsit Campus)

The Basic Knowledge Test is in TWO parts:

70 % of applicants FAIL the Group Written Test because they think they don't need to prepare!!!
ANNOUNCING BASIC KNOWLEDGE TEST RESULTS & NAME LIST FOR THE INTERVIEW BY THE THAI PILOT SELECTION COMMITTEE: Please check date at www.thaiairways.com
INTERVIEW BY THE THAI PILOT SELECTION COMMITTEE ON THE 16th FLOOR, CHAOPHYA PARK HOTEL, 247, RACHADAPISEK ROAD: Please check date at www.thaiairways.com

ANNOUNCING INTERVIEW BY THE THAI PILOT SELECTION COMMITTEE RESULTS & NAME LIST FOR THE MEDICAL TEST: Please check date at www.thaiairways.com

MEDICAL TEST AT THE INSTITUTE OF AVIATION MEDICINE, ROYAL THAI AIR FORCE (NEXT TO BHUMIPHOL ADULYADEJ HOSPITAL), 171, PAHOLYOTHIN ROAD: Please check dates at www.thaiairways.com

Applicants who have a pre-Lasik eye certificate of more than 300 will have very little chance of passing the Medical Examination!
ANNOUNCING MEDICAL TEST RESULTS & NAME LIST FOR THE APTITUDE TEST: Please check date at www.thaiairways.com

APTITUDE TEST (GROUP/WRITTEN), 08:30 - 17:00, AT SOFITEL CENTRAL PLAZA HOTEL, VIBHAVADI-RANGSIT ROAD: Please check date at www.thaiairways.com

ANNOUNCING APTITUDE TEST RESULTS & NAME LIST FOR THE TEAMWORK EXERCISES: Please check date at www.thaiairways.com
TEAMWORK EXERCISES, 08:30 - 17:00, AT THE RACHAVIPHA ROOM OR RACHADA 1 ROOM, CHAOPHYA PARK HOTEL, 247, RACHADAPISEK ROAD: Please check date at www.thaiairways.com

ANNOUNCING RESULTS OF THE TEAMWORK EXERCISES & NAME LIST FOR THE PSYCHOLOGICAL INTERVIEW(S): Please check date at www.thaiairways.com
PSYCHOLOGICAL INTERVIEW(S) ON THE 16th FLOOR, CHAOPHYA PARK HOTEL, 247, RACHADAPISEK ROAD: Please check dates at www.thaiairways.com

ANNOUNCING PSYCHOLOGICAL INTERVIEW(S) RESULTS & NAME LIST FOR THE AVIATION PSYCHOLOGICAL TESTS: Please check dates at www.thaiairways.com
AVIATION PSYCHOLOGICAL GROUP TEST, 08:00 - 12:00, AT BRIEFING ROOM No. 1, 3rd FLOOR, THE INSTITUTE OF AVIATION MEDICINE, BHUMIPHOL ADULYADEJ HOSPITAL, 171, PAHOLYOTHIN ROAD: Please check dates at www.thaiairways.com

AVIATION PSYCHOLOGICAL INDIVIDUAL TEST, 08:15 - 13:00, AT ROOM No, 171, PAHOLYOTHIN ROAD. 223, 2nd FLOOR, THE INSTITUTE OF AVIATION MEDICINE, BHUMIPHOL ADULYADEJ HOSPITAL: Please check dates at www.thaiairways.com
ANNOUNCING FINAL RESULT: Please check date at www.thaiairways.com

ORIENTATION & CONTRACT SIGNING FOR NEW EMPLOYEES: Please check date at www.thaiairways.com

|
TG Qualified Pilot Schedule 2024

ADVERTISEMENT: Please check dates at www.thaiairways.com
The requirements are as follows:

Note: If you are not sure Thai Airways International recognises your flying school, then please contact Thai Airways' Flight Operations Department.

Important: Please make sure you refer to and follow Articles 6, 7, and 9 of the Civil Aviation Board's regulations Number 75 within 90 days of the application date.

Note: Applicants who failed the Aptitude Test are not allowed to reapply until after a three-year period.

RECEIVING ONLINE APPLICATIONS: Please check dates at www.thaiairways.com
Applicants must log on to: www.thaiairways.com
ANNOUNCING APPLICATION SUBMISSION APPOINTMENTS: Please check dates at www.thaiairways.com

RECEIVING APPLICATIONS: Please check dates at www.thaiairways.com

Applicants must provide originals of all documents and one photocopy of each document.

Applicants with fake or fraudulently obtained military service exemption certificates will not be allowed to test.
ANNOUNCING NAMES OF APPLICANTS ELIGIBLE FOR THE BASIC KNOWLEDGE TEST: Please check date at www.thaiairways.com
BASIC KNOWLEDGE TEST (08:00 - 12:30) AT ROOM 3111 OR 3112, 11th FLOOR, BUILDING No. 3, THAI HEAD OFFICE, 89, VIBHAVADI-RANGSIT ROAD: Please check date at www.thaiairways.com
The Basic Knowledge Test is in TWO parts:

A LOT of qualified pilots FAIL the Group Written Test because they think they don't need to prepare!!!
ANNOUNCING BASIC KNOWLEDGE TEST RESULTS & NAME LIST FOR THE INTERVIEW BY THE THAI PILOT SELECTION COMMITTEE: Please check date at www.thaiairways.com
INTERVIEW BY THE THAI PILOT SELECTION COMMITTEE AT 16th FLOOR, CHAOPHYA PARK HOTEL, 247, RACHADAPISEK ROAD: Please check date at www.thaiairways.com

ANNOUNCING INTERVIEW BY THE THAI PILOT SELECTION COMMITTEE RESULTS & NAME LIST FOR THE APTITUDE TEST: Please check date at www.thaiairways.com
APTITUDE TEST (GROUP/WRITTEN), 08:30 - 17:30, AT ROOM 3111 OR 3112, 11th FLOOR, BUILDING No. 3, THAI HEAD OFFICE, 89, VIBHAVADI-RANGSIT ROAD: Please check date at www.thaiairways.com

ANNOUNCING APTITUDE TEST RESULTS & NAME LIST FOR THE TEAMWORK EXERCISES: Please check date at www.thaiairways.com
TEAMWORK EXERCISES, 08:30 - 17:30, AT THE RACHAVIPHA ROOM OR RACHADA 1 ROOM, CHAOPHYA PARK HOTEL, 247, RACHADAPISEK ROAD: Please check date at www.thaiairways.com

ANNOUNCING RESULTS OF THE TEAMWORK EXERCISES & NAME LIST FOR THE PSYCHOLOGICAL INTERVIEW (S): Please check date(s) at www.thaiairways.com
PSYCHOLOGICAL INTERVIEW (S) ON THE 16th FLOOR, CHAOPHYA PARK HOTEL, 247, RACHADAPISEK ROAD: Please check dates at www.thaiairways.com

PROFICIENCY RIDE CHECK, THAI HEAD OFFICE, 89, VIBHAVADI-RANGSIT ROAD: Please check date at www.thaiairways.com
ANNOUNCING FINAL RESULT: Please check date at www.thaiairways.com

ORIENTATION & CONTRACT SIGNING FOR NEW EMPLOYEES: Please check date at www.thaiairways.com
|
Aptitude Test

- The Aptitude Test (skill test) is one of the most important steps. Thai Airways must be sure that an applicant is suitable for the job of pilot, he has the potential to learn to fly under normal and critical stressful conditions, and that he can take responsibility for flight safety, security, equipment, and most importantly, people's lives.
- The Aptitude Test is controlled by behavioural scientists & psychologists from the Scandinavian Institute of Aviation Psychology (SIAP).
- The Aptitude Test is a 4 to 5-hour English language written test. Wide-ranging skills are tested. These include aviation knowledge,

natural science, instrument comprehension, maths, quality & speed of perception (the ability to quickly & accurately perceive & realise complex information - facts, events, situations, ...), spatial orientation (the ability to quickly & safely understand how to move, or navigate, in the three dimensions of space), logic & mechanical comprehension (testing of applicants' general understanding of forces & dynamics in natural science), numerical analysis, sense of locality, analytical & logical reasoning (the ability to quickly & accurately follow & analyse information processes, & use logic to find new information and next steps), tests to follow & process complex information, rational reasoning, short-term memory (the ability to understand information, memorise it in a short time, & later write down the most important parts of it), and speed, accuracy, & problem solving tests.
- Please remember! A pilot is a normal person, he is not Mr. Perfect. For this reason, Thai Airways will not choose people with perfect skills. The important thing is that you have normal skills and that your skill level balances over a wide range.
FILL-IN-THE-BLANKS, QUESTION & ANSWER, BIOGRAPHY

- Before applicants can go home in the afternoon, they must complete the following written tests:
- Fill in the Blanks:
- Applicants must fill in basic information (for example, my name is ...) and give their opinions about many subjects (for example, their performance in the Aptitude Test and their motivation to join Thai Airways international).
- Question & Answer:
- Applicants have many questions to answer. They must write short answers about their basic life history, their educational training, their previous & present family patterns, their social life outside of education, work, ...

- Biography:
- Applicants must write some short paragraphs (maximum 1 page) about their basic life history. Applicants can include anything they think is useful to their pilot application.
Teamwork Tests

- Groups of 6 applicants sit around tables together. Each group is given information and instructions about 1, sometimes 2, complex situations. Applicants must analyse the situation, suggest ideas, solve problems, and make decisions.
- With some activities, the psychologists will give each person only some of the information needed to complete the whole activity. It is then up to each applicant to analyse the situation, share his information, suggest ideas, solve problems, and make decisions based on knowledge, experience, and logical reasoning.

- The psychologists will watch everyone's performance and evaluate candidates to see how they cooperate, communicate, and collaborate together. The ability to work in a team and execute leadership is essential in modern cockpits. They will observe who is not confident, who is creative and full of ideas, who takes initiatives, who is not enthusiastic, who is emotionally out of control, who is lacking behind, ...
- Important evaluation areas include Cooperation / Teamwork, Capacity & Attitude, Initiative / Pro-activity, Leadership, Drive / Motivation, Goal Orientation, Attentiveness, Decision Making, and Communication Skills.
- Applicants must focus on working together and helping each other. Do not worry if your group cannot complete the activity in time. It is not the objective of the Teamwork Exercises.

- Creative Thinking (Mental Flexibility) is a very important pilot quality. If a good pilot has a problem, but he can think widely (this includes indirect ideas), it is very possible he can find an answer. The situations and problems in the Teamwork Exercises have no right or wrong answers. Try not to think about the normal rigid direct ideas. Try to relax your thinking, and think about opposite or indirect ideas, but have reason! Your ideas will score points with the psychologists!
- The Teamwork Exercises are some of the most important tests. You cannot get them wrong! The Teamwork Exercises are the first time the psychologists will watch you directly. If you do badly in the Teamwork Exercises, it is possible you can still pass the Teamwork Exercises, but the result might later affect your Psychological Interviews.
- The results of the Teamwork Exercises will be announced on the scheduled date by the Flight Crew Recruitment Department Manager, Aviation Personnel Development Section, TG Flight Operations Department.
- The Flight Crew Recruitment Department Manager will also inform all successful applicants of the date and times of their Individual Psychological Interview(s) & Examinations, as well as the name(s) of the psychologist(s) they will interview with.
INDIVIDUAL PSYCHOLOGICAL INTERVIEW(S) & EXAMINATIONS, WALKING TEST(S), COMPUTER-BASED ABILITY TEST, & JOYSTICK TEST
Before the Individual Psychological Interview(s), all applicants must test the following:
- Walking Test(s):
- All applicants will have one or more Walking Tests (Psychometric Tests). A pilot must do many things at the same time and make accurate decisions, often under a lot of pressure. The objective of this test is to check that applicants can do the same.
- If an applicant over prepares and makes the Walking Test look too easy, the psychologist will give him a more difficult Walking Test to do!
- All applicants will have one or more Walking Tests (Psychometric Tests). A pilot must do many things at the same time and make accurate decisions, often under a lot of pressure. The objective of this test is to check that applicants can do the same.

- Computer-Based Pilot Ability Test:
- All applicants will have a Computer-Based Pilot Ability Test. There are now MANY designs of Computer-Based Pilot Ability Test.
- All of the Computer-Based Pilot Ability Tests check similar things, for example, an applicants' stress tolerance, his ability to handle high workloads, comprehend, memorise, and process complex & confusing information (spatial ability), calculate mathematics quickly and accurately when under a lot of pressure, stay vigilant and alert, do many things at the same time (simultaneous capacity), and make accurate decisions.
- Applicants cannot see it, but they have a camera to check the reactions on the applicant's face when he must handle high workloads, and work quickly and accurately under pressure. Again, be careful of what you show the psychologist, not what you say! The psychologist will also observe you from behind, so be careful about your body language!

- Joystick Test:
- All applicants will have a Joystick Test(s). This is another test to check an applicant's ability to do many things at the same time under stress. In this test, applicants need to become very alert and very focused. Applicants use a joystick to move a circle over a cross, but the joystick is very sensitive. For example, if an applicant pushes the joystick left too much, the circle will move around and around. It is better to make small movements to the joystick to show the psychologist that you are in control! At the same time, applicants must listen, analyse and process sometimes complex information, and answer questions, including maths.
- The psychologist will observe you at the same time, so again, be careful about your face and what your face shows the psychologist! Keep your face emotionless. Keep all feelings inside. What you say is less important!
INDIVIDUAL PSYCHOLOGICAL INTERVIEW(S)

- All successful applicants will have one, or possibly two, Individual Psychological Interview(s). This is the most important step of the TG pilot selection process.
- The interview is about 30 - 40 minutes. The interview allows the psychologist (professor) to get a general impression of the applicant's life. The psychologist (professor) will evaluate the information collected from all the previous steps, and investigate important events in the applicant's life, his way of thinking and working, his flying experience, his attitudes and goals, his social interaction patterns, and a lot more.

- Most Thai applicants have never experienced psychological interviews and very few people have interviewed in English. This creates a lot of fear and apprehension among many Thai applicants, but it is a very important step. The psychologists have many years of experience. They understand how people feel. They make sure that everyone has fair and equal opportunity to succeed. The psychologists will make sure they have an accurate assessment of the strengths and weaknesses of every applicant's capabilities, and of his potential to be a good and safe pilot.

- A lot of people think that a psychological interview is the same as a normal job interview. NO! A lot of people also think that if they give good answers, they can pass. NO! Psychology is not about this. The main reason psychologists ask you about your life is not because they want to know about your life! The main reason is that when you answer their questions, they can watch, and focus on the way you present and show yourself. This is the important thing. So do not focus too much on your answers, focus on what you show the psychologist(s) and how you present yourself (confident, not confident, enthusiastic, not enthusiastic, positive, negative, in control, weak, relaxed, serious, ...). Also do not lie to the psychologists! Don't try to be the 'perfect pilot'. Just be yourself, stay open-minded, and try to relax and enjoy the interview(s). The psychologists will not eat you!
GOOD PILOTS
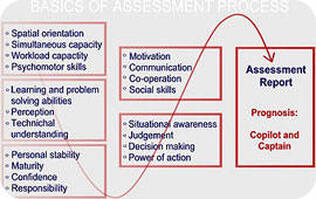
- Good Pilots accept that mistakes can happen and they know they can improve themselves. If something happens, good pilots detect the mistake immediately. Good pilots stay calm while they deal with and correct mistakes.
- Good Pilots do not allow mistakes to affect their confidence or increase the number of mistakes. They also do not allow mistakes to affect their ability to deal with mistakes. They keep an optimistic attitude towards problems and mistakes.
- Good Pilots develop good and safe ways of thinking. They stay alert for possible problems and try to ‘see’ a problem before it happens. If a problem happens, they react fast, communicate the problem to the other pilot, and take decisive action before the problem becomes serious.
- Good Pilots must have Leadership and Judgement. Safety depends on a pilot's decisions. Pilots need to have the confidence to make difficult decisions and take decisive action in uncertain situations. In some situations, there is insufficient time to ask the other pilot. A pilot needs to think and react quickly. He must make decisions by himself and be strong enough to finish what he starts.
- Good Pilots must have Trust. A captain often works with co-pilots he has never met. They must trust and cooperate with each other, and quickly build good teamwork and a strong relationship. Safety depends on it.
- Good Pilots must have Maturity. To become more mature, you need to analyse yourself. What is good about you? What is not good about you? What do you need to improve? More maturity will help a pilot to better manage himself and his crew.
- Good Pilots must have Stress Coping Ability. Trust, energy, and maturity will help a pilot to better cope with stress. This will help to increase situational awareness and, most importantly, safety.
- Good Pilots must have Communication Ability. Safety depends on clear understandable communication between captain and co-pilot.
- Good Pilots will say NO if they are unsure of the situation. They will NOT continue despite the pressure the airlines put on the pilots to continue and complete the flight. They must know when something is right or wrong. Safety depends on it.
- Good Pilots change themselves quickly, so that they can deal with the pressure and the working conditions of the job. Good pilots listen to their team. They are open-minded to changes, and are motivated to learn and improve themselves. The job of pilot is a never-ending learning process. There is always something new to learn that can increase safety.
- Good Pilots have a positive effect on passengers and crew; they help passengers and crew to stay calm when a situation becomes serious and there are disagreements about the best thing to do.

It is very difficult for a good pilot to have everything mentioned above, but if he can improve himself in the areas mentioned above, he can also improve his situational awareness, and his suitability for a career as a service industry commercial airline pilot.

THAI AIRWAYS PILOT SELECTION BOARD MEETING

- After the Individual Psychological Interview(s) & Examinations are finished, the psychologists will discuss every applicant from different views. They will write assessment reports on every applicant. These reports include observations, decisions, conclusions, and a final recommendation on every applicant. Every applicant will also have two sets of scores, ranging from one to nine (one = poor, five = average, nine = excellent). The first set of scores predicts an applicant's ability to become a TG First Officer (co-pilot). The second set of scores predicts an applicant's ability to develop himself to become a TG Pilot Commander (captain).
- The psychologists will also write a Final Report on every applicant. This report has three parts: General Background, Personality and Resources Profile, and Conclusions and Recommendations. The Final Report also includes a special Personality Profile. This is a summary of many important parts of an applicant's personality, for example, an applicant's motivation to apply for TG commercial pilot, basic capability resources, and social and personality patterns. This special Personality Profile is displayed as a set of scores, ranging from one to nine (one = poor, five = average, nine = excellent).
- The final results and recommendations are presented at the Thai Airways Pilot Selection Board Meeting at the THAI Head Office. The Selection Board will carefully review the final results and recommendations, and make its own final decision.

USEFUL WEBSITES
SELECTION OF CIVIL AVIATION PILOTS

บทบาทของนักบินในปัจจุบันเป็นผู้ควบคุม Technical systems และ บริหาร Human sources ในหลากหลายรูปแบบ เพื่อให้ Flight ดำเนินไปอย่างปลอดภัยและมีประสิทธิภาพ
การบินในยุคต้นๆ หน้าที่หลักของนักบิน คือ Manual control ACFT และประสานงานกับผู้ที่เกี่ยวข้อง แต่ปัจจุบันนักบินทำหน้าที่ Monitor และ cross-check สภาพการบินต่างๆ ที่เปลี่ยนแปลงไปตามเวลา และ ACFT system ที่มีผลมาจากสภาพแวดล้อม นักบินจะใช้ข้อมูลเหล่านี้มาเป็นพื้นฐานในการตัดสินใจ ภายใต้เวลาที่กำหนด ทั้งนี้นักบินจะต้องปรึกษาลูกเรือที่เกี่ยวข้อง ก่อนดำเนินการแก้ไข ความปลอดภัยจึงขึ้นอยู่กับ
ดังนั้นการเลือกนักบินในปัจจุบันจะคำนึงถึงคุณสมบัติเหล่านี้
เข้าใจหลักการทาง Mechanical, technical และ physical เห็นภาพ หรือ วาดภาพแล้วประเมินผลได้
มีความสามารถในทางคำนวณ มีระเบียบแบบแผนในการคิดหาคำตอบทางตัวเลขโดยประมาณอย่างมีเหตุผล (Logical reasoning)
Short-term memory ดี สามารถจับใจความสำคัญ และ เอาออกมาใช้ได้
มีความรวดเร็วในการมองเห็นข้อแตกต่างอย่างลึกซึ้ง
มีสมาธิในการทำงานโดยไม่วอกแวกกับสิ่งเร้าอื่นๆ ทั้งภายนอกและทางจิตใจ เมื่อมีงานอื่นมาประกอบหลายอย่าง ก็สามารถแบ่งสมาธิไปทำงานนั้นพร้อมๆกับทำงานหลัก กลับไปกลับมาได้
มีมุมมองที่กว้างไกล มองเห็นความสัมพันธ์ของสิ่งต่างๆในหลายมุมมองได้ ทราบว่าผู้เกี่ยวข้องที่มีฐานะต่างกัน มีมุมมอง และ ความสัมพันธ์ต่อเหตุการณ์นั้นๆอย่างไร และ มุมมองเหล่านี้เปลี่ยนแปลงเมื่อฐานะและความสัมพันธ์ของผู้เกี่ยวข้องเปลี่ยนไป
ตกลงตัดสินใจ และ แก้ไขทันต่อเหตุการณ์อย่างมีเหตุผล
Eye-hand-feet co-ordination : ควบคุมมือเท้าได้ดี ตามข้อมูลที่ได้จากการเห็น การฟังที่เปลี่ยนแปลงตลอดเวลา
ทำงานหลายอย่างที่มีกิจกรรม และ ขบวนการต่างกันอย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ พร้อมๆกัน ทั้งสามารถเลือกจัดลำดับความสำคัญของงานนั้นๆได้
การสอบภาษาอังกฤษขึ้นอยู่กับภาษาประจำวันของผู้สมัคร อุปกรณ์ใช้ทดสอบ Multiple-task capacity และ eye-hand-feet coordination ( Psychomotor ) มีประสิทธิภาพมากเมื่อนำไปทดสอบร่วมกับ Flexible possibilities ในสถานะการณ์ที่กำหนดให้ พร้อมๆกับ Multiple task test จะสามารถพยากรณ์ pilot performance ได้
จาก accident / incident investigation พบว่า การขัดแย้งใน cockpit นำไปสู่การตัดสินใจที่ขาดเหตุผลและไม่ถูกต้องตามกฎ ขณะ training ก็ทำตามกฎระเบียบ ปฏิบัติ แต่พอปล่อยออกไปแล้ว ตอน line operation กลับทำอีกอย่างตามใจตัวเอง Pilot skill ที่ train ขึ้นมานั้น สำคัญกว่า personality characteristics มาก การใช้ Home made procedure ในการบินเป็นอันตรายที่สุด โดยเฉพาะในช่วง " honeymoon effect " เพราะจะมีการแหกกฎมากในช่วงนั้น เนื่องจากมีความเกรงใจสูง ( Capt. และ Co-pilot ใหม่บินด้วยกัน )
case ที่แก้ไขยากที่สุดคือ pilots ไม่ ปฏิบัติตาม Company procedures. " They are always in conflict with others. " ในขณะที่ " Deficits in pure pilot skills can often be compensated by additional training. " นิสัยถาวรนั้นแก้ยาก ทางป้องกันที่ดี คือ ต้องคัดบุคคลเหล่านี้ออก โดยใช้นักจิตวิทยาเป็นผู้วินิจฉัย
กรรมวิธีในการวินิจฉัยจะประกอบไปด้วย
และ รุนแรง เรียกว่าเพี้ยนนิด เพี้ยนหน่อย จิตแพทย์ก็จะเอาตกหมด แต่ถ้าใครผ่านได้ก็เจ๋ง
มาตรการที่นักจิตวิทยาใช้พิจารณาลักษณะท่าทาง และ อุปนิสัยของผู้สมัครประกอบไปด้วย
การบินในยุคต้นๆ หน้าที่หลักของนักบิน คือ Manual control ACFT และประสานงานกับผู้ที่เกี่ยวข้อง แต่ปัจจุบันนักบินทำหน้าที่ Monitor และ cross-check สภาพการบินต่างๆ ที่เปลี่ยนแปลงไปตามเวลา และ ACFT system ที่มีผลมาจากสภาพแวดล้อม นักบินจะใช้ข้อมูลเหล่านี้มาเป็นพื้นฐานในการตัดสินใจ ภายใต้เวลาที่กำหนด ทั้งนี้นักบินจะต้องปรึกษาลูกเรือที่เกี่ยวข้อง ก่อนดำเนินการแก้ไข ความปลอดภัยจึงขึ้นอยู่กับ
- The crew - ACFT interface
- The crew - Crew interface
ดังนั้นการเลือกนักบินในปัจจุบันจะคำนึงถึงคุณสมบัติเหล่านี้
- ความรับรู้และมีเหตุผล
- รู้เรื่องเครื่องยนต์กลไก
- ความสามารถในการบริหารจัดการ
- สังคมให้การตอบสนองในทางที่ดี
เข้าใจหลักการทาง Mechanical, technical และ physical เห็นภาพ หรือ วาดภาพแล้วประเมินผลได้
มีความสามารถในทางคำนวณ มีระเบียบแบบแผนในการคิดหาคำตอบทางตัวเลขโดยประมาณอย่างมีเหตุผล (Logical reasoning)
Short-term memory ดี สามารถจับใจความสำคัญ และ เอาออกมาใช้ได้
มีความรวดเร็วในการมองเห็นข้อแตกต่างอย่างลึกซึ้ง
มีสมาธิในการทำงานโดยไม่วอกแวกกับสิ่งเร้าอื่นๆ ทั้งภายนอกและทางจิตใจ เมื่อมีงานอื่นมาประกอบหลายอย่าง ก็สามารถแบ่งสมาธิไปทำงานนั้นพร้อมๆกับทำงานหลัก กลับไปกลับมาได้
มีมุมมองที่กว้างไกล มองเห็นความสัมพันธ์ของสิ่งต่างๆในหลายมุมมองได้ ทราบว่าผู้เกี่ยวข้องที่มีฐานะต่างกัน มีมุมมอง และ ความสัมพันธ์ต่อเหตุการณ์นั้นๆอย่างไร และ มุมมองเหล่านี้เปลี่ยนแปลงเมื่อฐานะและความสัมพันธ์ของผู้เกี่ยวข้องเปลี่ยนไป
ตกลงตัดสินใจ และ แก้ไขทันต่อเหตุการณ์อย่างมีเหตุผล
Eye-hand-feet co-ordination : ควบคุมมือเท้าได้ดี ตามข้อมูลที่ได้จากการเห็น การฟังที่เปลี่ยนแปลงตลอดเวลา
ทำงานหลายอย่างที่มีกิจกรรม และ ขบวนการต่างกันอย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ พร้อมๆกัน ทั้งสามารถเลือกจัดลำดับความสำคัญของงานนั้นๆได้
การสอบภาษาอังกฤษขึ้นอยู่กับภาษาประจำวันของผู้สมัคร อุปกรณ์ใช้ทดสอบ Multiple-task capacity และ eye-hand-feet coordination ( Psychomotor ) มีประสิทธิภาพมากเมื่อนำไปทดสอบร่วมกับ Flexible possibilities ในสถานะการณ์ที่กำหนดให้ พร้อมๆกับ Multiple task test จะสามารถพยากรณ์ pilot performance ได้
จาก accident / incident investigation พบว่า การขัดแย้งใน cockpit นำไปสู่การตัดสินใจที่ขาดเหตุผลและไม่ถูกต้องตามกฎ ขณะ training ก็ทำตามกฎระเบียบ ปฏิบัติ แต่พอปล่อยออกไปแล้ว ตอน line operation กลับทำอีกอย่างตามใจตัวเอง Pilot skill ที่ train ขึ้นมานั้น สำคัญกว่า personality characteristics มาก การใช้ Home made procedure ในการบินเป็นอันตรายที่สุด โดยเฉพาะในช่วง " honeymoon effect " เพราะจะมีการแหกกฎมากในช่วงนั้น เนื่องจากมีความเกรงใจสูง ( Capt. และ Co-pilot ใหม่บินด้วยกัน )
case ที่แก้ไขยากที่สุดคือ pilots ไม่ ปฏิบัติตาม Company procedures. " They are always in conflict with others. " ในขณะที่ " Deficits in pure pilot skills can often be compensated by additional training. " นิสัยถาวรนั้นแก้ยาก ทางป้องกันที่ดี คือ ต้องคัดบุคคลเหล่านี้ออก โดยใช้นักจิตวิทยาเป็นผู้วินิจฉัย
กรรมวิธีในการวินิจฉัยจะประกอบไปด้วย
- Past behaviour โดยศึกษาจากประวัติของบุคคลนั้น
- Questionnaires เพื่อหามุมมองของบุคคลนั้น
- Behaviour observation ดูปฏิกริยาโต้ตอบ เมื่อมีความขัดแย้ง
- การสัมภาษณ์ เพื่อนำมาเปรียบเทียบกับข้อมูลอื่นๆ
และ รุนแรง เรียกว่าเพี้ยนนิด เพี้ยนหน่อย จิตแพทย์ก็จะเอาตกหมด แต่ถ้าใครผ่านได้ก็เจ๋ง
มาตรการที่นักจิตวิทยาใช้พิจารณาลักษณะท่าทาง และ อุปนิสัยของผู้สมัครประกอบไปด้วย

N - Neuroticism มีความรู้สึกอ่อนไหว ขี้สงสาร ใจอ่อน
E - Extraversion เป็นคนเปิดเผย มีความเป็นมิตร
O - Openness to experience ไม่หวงวิชา
C - Conscientiousness ซื่อสัตย์ต่อหน้าที่
A - Agreeableness ตกลงกันได้ง่าย ไม่ยักท่า ไม่ยึกยัก
โดยทั่วๆไป successful pilot จะมีลักษณะ
การคัดเลือกนักบินแบบนี้เกณฑ์ผ่านหรือไม่ผ่าน ใช้การตัดสินจากประสบการณ์ที่ได้มาจาก Flight training โดยตรง การวิเคราะห์จะนำผล ความรู้ทางวิชาการ และ Aptitude test มาเปรียบเทียบกับผลการฝึก ปรากฎผลออกมาว่า จะมีนักบิน 2 กลุ่ม คือ
Standard career progress และ Marginal progress ทั้งสองกลุ่มนี้มีลักษณะต่างกันที่เห็นได้ชัดบางประการ
demand บางครั้งอาจต้อง "Higher aggressive " ก็เพียงเพื่อให้งานสำเร็จ ผู้ที่มี " well-balanced personality " จะสามารถเลือกใช้ลักษณะเฉพาะตัวให้เหมาะกับสถานะการณ์ ได้โดยไม่ต้องมีอิทธิพลใดมาครอบงำ ( พี่ไม่ต้อง น้องทำเอง )
Questionnaire นั้นมีจุดอ่อน ใคร smart ก็ตอบได้สบายๆ สร้างความประทับใจให้กรรมการ ดังนั้นการสัมภาษณ์ และ เฝ้าสังเกตุอุปนิสัยจึงต้องทำด้วยความปราณีต ปัจจุบันได้มี techniques ที่จะใช้วินิจฉัย "Actual behaviour" ของผู้สมัครแล้ว โดยดูการทำงานในขณะเข้าสถานการณ์ ทั้ง individual และเป็น group ผู้สมัครจะถูกใช้ให้ทำงานต่างๆชนิดกัน โดยทำหน้าที่ในบทบาทต่างๆ ( เป็นนายบ้าง เป็นลูกน้องบ้าง เป็นเพื่อนร่วมงานบ้าง ) และดูพฤติกรรมในขณะทำหน้าที่ต่างๆเหล่านั้น แล้วนำมาประเมินผล การทำงานเป็น group ( กลุ่มละ 3/6 คน ) แล้วให้ทำงานที่ต้องขัดแย้งกัน พฤติกรรมที่ไม่พึงประสงค์ คือ เมื่อขัดแย้งกันก็ไม่
ควรท้อแท้ ถอดใจไม่สู้ หรือข่มขู่ ก้าวร้าว ผู้ที่มีความเห็นแตกต่างจากตัวเอง ( เอางี้ก็แล้วกัน ) จุดประสงค์ ก็คือ ต้องรับฟังความคิดเห็นของผู้อื่น เมื่อถูกพาดพิง หรือ กล่าวหาก็ชี้แจงเหตุผลให้หายสงสัย โน้มน้าว หาเหตุผลสนับสนุนชักจูงให้ผู้อื่นคล้อยตาม มีทักษะในการเจรจาต่อรอง มีความสามารถในการประณีประนอมตามสภาพเหตุการณ์ จากนั้นก็ให้ทำงานเป็นหมู่เดียวกัน ประชุมร่วมกัน หารือแก้เหตุการณ์ที่สมมุติขึ้นภายใต้เวลาที่กำหนด การตัดสินใจจะทำได้ยาก เพราะเป็น incomplete information และ สภาวะแวดล้อมเปลี่ยนแปลงตลอดเวลา ทั้งนี้เพื่อทดสอบการทำงานภายใต้ความกดดัน ความเครียด ความไม่แน่นอน เพื่อดูความอดทนในการรับความเสี่ยง และ ความสามารถในการวิเคราะห์สถานะการณ์ และ ปรับตัวตามสภาพแวดล้อมที่เปลี่ยนแปลงตลอดเวลา
ใน individual exercise ผู้สมัครจะถูกทดสอบให้แก้ปัญหา flight preparation และ in flight problem ซึ่งผู้สมัครจะต้องแสดงถึง skill for planning, organising, decision making and task delegation อาจมีการทดลองให้ทำ public relation ประกาศให้ผู้โดยสารทราบ เรื่อง flight delay หรือ flight มีปัญหาทางด้าน service การประกาศนั้นจะต้องทำให้สมเหตุสมผล มีความเข้าใจ และ เอื้ออาทรต่อความต้องการของผู้โดยสาร ประกาศแล้วให้ผลสะท้อนกลับมาในทาง positive จากนั้นผู้สมัครจะถูกพาเข้าสู่ social conflict situation เพื่อทดสอบ ความอดทนต่อสภาพขัดแย้ง โดยสามารถทำงานในสภาพขัดแย้งได้อย่างมั่นใจ และ มีความอ่อนตัวที่จะรับข้อมูลใหม่ แล้วนำมาปรับแนวคิดของตนเอง การตัดสินว่าผ่านหรือไม่ จะต้องใช้ผู้ตัดสินอย่างน้อย 2 คน จึงจะได้ข้อมูลเพียงพอในการประเมินผล การตัดสินในหัวข้อต่างๆจะใช้วิธีให้ค่าเป็น yes หรือ no เด็ดขาดไปเลย
ปัจจุบัน Lufthansa แบ่งการสอบเป็น 4 วัน
E - Extraversion เป็นคนเปิดเผย มีความเป็นมิตร
O - Openness to experience ไม่หวงวิชา
C - Conscientiousness ซื่อสัตย์ต่อหน้าที่
A - Agreeableness ตกลงกันได้ง่าย ไม่ยักท่า ไม่ยึกยัก
โดยทั่วๆไป successful pilot จะมีลักษณะ
- ความเชื่อมั่นในตัวเองสูง
- อารมณ์คงที่หนักแน่น
- เป็นคนเปิดเผย และ มีความเป็นมิตร
การคัดเลือกนักบินแบบนี้เกณฑ์ผ่านหรือไม่ผ่าน ใช้การตัดสินจากประสบการณ์ที่ได้มาจาก Flight training โดยตรง การวิเคราะห์จะนำผล ความรู้ทางวิชาการ และ Aptitude test มาเปรียบเทียบกับผลการฝึก ปรากฎผลออกมาว่า จะมีนักบิน 2 กลุ่ม คือ
Standard career progress และ Marginal progress ทั้งสองกลุ่มนี้มีลักษณะต่างกันที่เห็นได้ชัดบางประการ
- Standard group คะแนนของ group นี้ที่ได้จากการทดสอบในภาคต่างๆ จะอยู่ใกล้เคียงกัน (average scores) ในขณะที่ marginal group คะแนนจะไปสุดโต่งบ่อยกว่า (ชอบใจก็เรียน ไม่ชอบใจก็ไม่เรียนอะไรประมานนั้น)
- Marginal group อารมณ์เปลี่ยนแปลงง่ายกว่า ความมีชีวิตชีวาน้อยกว่า ก้าวร้าวกว่า แก้ตัวเก่ง โทษโน่น โทษนี่ บางโอกาสใช้อารมณ์มากกว่าเหตุผล
demand บางครั้งอาจต้อง "Higher aggressive " ก็เพียงเพื่อให้งานสำเร็จ ผู้ที่มี " well-balanced personality " จะสามารถเลือกใช้ลักษณะเฉพาะตัวให้เหมาะกับสถานะการณ์ ได้โดยไม่ต้องมีอิทธิพลใดมาครอบงำ ( พี่ไม่ต้อง น้องทำเอง )
Questionnaire นั้นมีจุดอ่อน ใคร smart ก็ตอบได้สบายๆ สร้างความประทับใจให้กรรมการ ดังนั้นการสัมภาษณ์ และ เฝ้าสังเกตุอุปนิสัยจึงต้องทำด้วยความปราณีต ปัจจุบันได้มี techniques ที่จะใช้วินิจฉัย "Actual behaviour" ของผู้สมัครแล้ว โดยดูการทำงานในขณะเข้าสถานการณ์ ทั้ง individual และเป็น group ผู้สมัครจะถูกใช้ให้ทำงานต่างๆชนิดกัน โดยทำหน้าที่ในบทบาทต่างๆ ( เป็นนายบ้าง เป็นลูกน้องบ้าง เป็นเพื่อนร่วมงานบ้าง ) และดูพฤติกรรมในขณะทำหน้าที่ต่างๆเหล่านั้น แล้วนำมาประเมินผล การทำงานเป็น group ( กลุ่มละ 3/6 คน ) แล้วให้ทำงานที่ต้องขัดแย้งกัน พฤติกรรมที่ไม่พึงประสงค์ คือ เมื่อขัดแย้งกันก็ไม่
ควรท้อแท้ ถอดใจไม่สู้ หรือข่มขู่ ก้าวร้าว ผู้ที่มีความเห็นแตกต่างจากตัวเอง ( เอางี้ก็แล้วกัน ) จุดประสงค์ ก็คือ ต้องรับฟังความคิดเห็นของผู้อื่น เมื่อถูกพาดพิง หรือ กล่าวหาก็ชี้แจงเหตุผลให้หายสงสัย โน้มน้าว หาเหตุผลสนับสนุนชักจูงให้ผู้อื่นคล้อยตาม มีทักษะในการเจรจาต่อรอง มีความสามารถในการประณีประนอมตามสภาพเหตุการณ์ จากนั้นก็ให้ทำงานเป็นหมู่เดียวกัน ประชุมร่วมกัน หารือแก้เหตุการณ์ที่สมมุติขึ้นภายใต้เวลาที่กำหนด การตัดสินใจจะทำได้ยาก เพราะเป็น incomplete information และ สภาวะแวดล้อมเปลี่ยนแปลงตลอดเวลา ทั้งนี้เพื่อทดสอบการทำงานภายใต้ความกดดัน ความเครียด ความไม่แน่นอน เพื่อดูความอดทนในการรับความเสี่ยง และ ความสามารถในการวิเคราะห์สถานะการณ์ และ ปรับตัวตามสภาพแวดล้อมที่เปลี่ยนแปลงตลอดเวลา
ใน individual exercise ผู้สมัครจะถูกทดสอบให้แก้ปัญหา flight preparation และ in flight problem ซึ่งผู้สมัครจะต้องแสดงถึง skill for planning, organising, decision making and task delegation อาจมีการทดลองให้ทำ public relation ประกาศให้ผู้โดยสารทราบ เรื่อง flight delay หรือ flight มีปัญหาทางด้าน service การประกาศนั้นจะต้องทำให้สมเหตุสมผล มีความเข้าใจ และ เอื้ออาทรต่อความต้องการของผู้โดยสาร ประกาศแล้วให้ผลสะท้อนกลับมาในทาง positive จากนั้นผู้สมัครจะถูกพาเข้าสู่ social conflict situation เพื่อทดสอบ ความอดทนต่อสภาพขัดแย้ง โดยสามารถทำงานในสภาพขัดแย้งได้อย่างมั่นใจ และ มีความอ่อนตัวที่จะรับข้อมูลใหม่ แล้วนำมาปรับแนวคิดของตนเอง การตัดสินว่าผ่านหรือไม่ จะต้องใช้ผู้ตัดสินอย่างน้อย 2 คน จึงจะได้ข้อมูลเพียงพอในการประเมินผล การตัดสินในหัวข้อต่างๆจะใช้วิธีให้ค่าเป็น yes หรือ no เด็ดขาดไปเลย
ปัจจุบัน Lufthansa แบ่งการสอบเป็น 4 วัน

Day 1 - Paper-pencil test (Questionnaire)
Day 2 - Apparatus test (eye-hand-feet coordinate, aptitude)
Day 3 - Assessment centre (ประเมินสถานการณ์, social conflict management, ความมั่นคงทางอารมณ์)
Day 4 - Interview (ตรวจสอบขั้นสุดท้ายว่ามีความรู้ ความสามารถ เป็นไปตามที่ได้รับจาก Day 1, 2, 3 จริงหรือไม่)
ได้พบข้อเปรียบเทียบภายหลังว่าคะแนนการสอบเข้า และ rating จาก line-training สอดคล้องกัน ผู้ที่มี social skill ก็จะมี good coordination เป็นต้น
ในขณะนี้ assessment centre techniques เป็นวิธีที่ดีที่สุด สำหรับ pilot selection การแข่งขันทางสังคมสูงมาก ทำให้หาคนใจกว้างได้ยาก จึงต้องหาวิธีพยากรณ์ความประพฤติ " A powerful instrument for the selection of the most suitable candidates for teamwork and cooperation tasks in an airline cockpit. " และวิธีนี้ยุติธรรมที่สุด เพราะว่า "Applicants have a chance to prove themselves" หลักการเหล่านี้มีความสมเหตุสมผล หากจัดการให้สมบูรณ์แบบ จะช่วยลด cost และเวลาได้
Day 2 - Apparatus test (eye-hand-feet coordinate, aptitude)
Day 3 - Assessment centre (ประเมินสถานการณ์, social conflict management, ความมั่นคงทางอารมณ์)
Day 4 - Interview (ตรวจสอบขั้นสุดท้ายว่ามีความรู้ ความสามารถ เป็นไปตามที่ได้รับจาก Day 1, 2, 3 จริงหรือไม่)
ได้พบข้อเปรียบเทียบภายหลังว่าคะแนนการสอบเข้า และ rating จาก line-training สอดคล้องกัน ผู้ที่มี social skill ก็จะมี good coordination เป็นต้น
ในขณะนี้ assessment centre techniques เป็นวิธีที่ดีที่สุด สำหรับ pilot selection การแข่งขันทางสังคมสูงมาก ทำให้หาคนใจกว้างได้ยาก จึงต้องหาวิธีพยากรณ์ความประพฤติ " A powerful instrument for the selection of the most suitable candidates for teamwork and cooperation tasks in an airline cockpit. " และวิธีนี้ยุติธรรมที่สุด เพราะว่า "Applicants have a chance to prove themselves" หลักการเหล่านี้มีความสมเหตุสมผล หากจัดการให้สมบูรณ์แบบ จะช่วยลด cost และเวลาได้
THAI AIRWAYS PILOT TRAINING

After the ground school and flight school training at the Civil Aviation Training Centre (CATC) in Hua Hin, pilot candidates return to the Thai Airways Head Office for further pilot training. TG Pilot Training can be classified as follows:
1. Pilot Candidate Training 2. Promotion Training 3. Transition Training
4. Recurrent Training 5. Other Training
4. Recurrent Training 5. Other Training
PILOT CANDIDATE TRAINING

After the pilot selection process, pilot candidates still have a lot of education, training, and testing to do before they are allowed into the cockpit of a Thai Airways aircraft.
Basic Course: 24 weeks of intensive training. Pilot candidates study aerodynamics, commercial aircraft systems and performance, aviation weather, commercial aircraft flight management and navigation systems, English and communication, and company regulations, for example, the THAI Safety and Quality Manual (TSQM), and the THAI Flight Operations Manual (FOM). The Basic Course is also to teach pilot candidates practical airline operation, safety, quality, and the culture of THAI airline operations.
After pilot candidates successfully pass this course, they are allowed onto the flight deck of a Thai Airways aircraft. However, they still cannot sit at the controls. Pilot candidates observe the captain and co-pilot, and gain knowledge and experience on the THAI route net.
When supervisory pilots, instructor pilots, and senior line pilots think a pilot candidate is ready, he is sent on a Transition Course for a specific aircraft type. After a pilot candidate has completed that course, he will become a 'cruise pilot'. A 'cruise pilot' cannot control the aircraft while taking off and climbing and while descending and landing, but he is allowed to control the aircraft while cruising, cruising and climbing, and cruising and descending. This is also a way for the captain and co-pilot to take a break during non-critical parts of the flight.
At this stage, 'cruise pilots' can now think they are THAI pilots. However, before they can get real control of a Thai Airways aircraft, new pilots must get 1-2 years of experience, and be recommended for Promotion Training to unrestricted co-pilot duties (First Officer).
Basic Course: 24 weeks of intensive training. Pilot candidates study aerodynamics, commercial aircraft systems and performance, aviation weather, commercial aircraft flight management and navigation systems, English and communication, and company regulations, for example, the THAI Safety and Quality Manual (TSQM), and the THAI Flight Operations Manual (FOM). The Basic Course is also to teach pilot candidates practical airline operation, safety, quality, and the culture of THAI airline operations.
After pilot candidates successfully pass this course, they are allowed onto the flight deck of a Thai Airways aircraft. However, they still cannot sit at the controls. Pilot candidates observe the captain and co-pilot, and gain knowledge and experience on the THAI route net.
When supervisory pilots, instructor pilots, and senior line pilots think a pilot candidate is ready, he is sent on a Transition Course for a specific aircraft type. After a pilot candidate has completed that course, he will become a 'cruise pilot'. A 'cruise pilot' cannot control the aircraft while taking off and climbing and while descending and landing, but he is allowed to control the aircraft while cruising, cruising and climbing, and cruising and descending. This is also a way for the captain and co-pilot to take a break during non-critical parts of the flight.
At this stage, 'cruise pilots' can now think they are THAI pilots. However, before they can get real control of a Thai Airways aircraft, new pilots must get 1-2 years of experience, and be recommended for Promotion Training to unrestricted co-pilot duties (First Officer).
PROMOTION TRAINING

Promotion Training consists of:
1. 'Cruise Pilot' to First Officer
2. First Officer to Captain
'Cruise Pilot' to First Officer: After about 1-2 years as a 'cruise pilot', the Flight Operations Department will assess the suitability of a 'cruise pilot' to train to become a First Officer. His knowledge, skills, and general performance are all assessed.
After that, he studies a full transition course for one of the smaller THAI aircraft. He then starts flying as a co-pilot with instructors and supervisory captains for 2-3 months. After he has passed several checks and evaluations, he is released to unrestricted First Officer duties on the line. When he gains more experience, he will have a chance to train to fly larger aircraft in the THAI fleet.
First Officer to Captain: The goal of most THAI pilots is to become a captain. It is not an easy or fast road. One of the strictest and most comprehensive programmes in the airline industry is the selection, training, experience, and evaluations needed to become a Thai Airways International Captain. The basic requirements are 8 years flying experience, with at least 4 years as a First Officer. Pilots must also have an Airline Transport Pilot (ATP) Licence.
Candidates for Captain undergo a 3-5 month evaluation programme by a Flight Operations Panel. There are 6 evaluators who fly and work with the candidate. At the end of the evaluation period, all 6 evaluators must unanimously agree that the candidate is ready and he has the qualifications needed to become a Thai Airways Captain.
However, if a candidate is successful, Promotion Training will usually not start immediately. It depends on seniority and fleet expansion.
The Promotion Training itself is a full transition course for a smaller THAI aircraft. After a long period of operating experience, flying with experienced captains acting as co-pilots, he will finally reach his goal of becoming a Captain with Thai Airways. Usually Thai Airways pilots work at least 11 years before they are promoted to Captain.
1. 'Cruise Pilot' to First Officer
2. First Officer to Captain
'Cruise Pilot' to First Officer: After about 1-2 years as a 'cruise pilot', the Flight Operations Department will assess the suitability of a 'cruise pilot' to train to become a First Officer. His knowledge, skills, and general performance are all assessed.
After that, he studies a full transition course for one of the smaller THAI aircraft. He then starts flying as a co-pilot with instructors and supervisory captains for 2-3 months. After he has passed several checks and evaluations, he is released to unrestricted First Officer duties on the line. When he gains more experience, he will have a chance to train to fly larger aircraft in the THAI fleet.
First Officer to Captain: The goal of most THAI pilots is to become a captain. It is not an easy or fast road. One of the strictest and most comprehensive programmes in the airline industry is the selection, training, experience, and evaluations needed to become a Thai Airways International Captain. The basic requirements are 8 years flying experience, with at least 4 years as a First Officer. Pilots must also have an Airline Transport Pilot (ATP) Licence.
Candidates for Captain undergo a 3-5 month evaluation programme by a Flight Operations Panel. There are 6 evaluators who fly and work with the candidate. At the end of the evaluation period, all 6 evaluators must unanimously agree that the candidate is ready and he has the qualifications needed to become a Thai Airways Captain.
However, if a candidate is successful, Promotion Training will usually not start immediately. It depends on seniority and fleet expansion.
The Promotion Training itself is a full transition course for a smaller THAI aircraft. After a long period of operating experience, flying with experienced captains acting as co-pilots, he will finally reach his goal of becoming a Captain with Thai Airways. Usually Thai Airways pilots work at least 11 years before they are promoted to Captain.
TRANSITION TRAINING

Transition Training means training to fly a specific aircraft type in the Thai Airways aircraft fleet. Qualified instructors use training tools, for example, Computer-Based Training programmes (CBT), Cockpit Procedure Trainers (CPT), Fixed-Base Simulators (FBS), and Full Flight Simulators (FFS).
The Transition Training time varies with aircraft type, and depends on the complexity of the aircraft and its equipment.
During the Transition Training course, pilots learn to operate specific aircraft under normal, abnormal, and emergency conditions. The course also includes a comprehensive technical section. This covers aircraft systems, performance, and operating procedures.
Full and advanced Flight Simulators are used in the last part of the training. This covers normal, abnormal, and emergency situations in-flight and on the ground. Realistic LOFT (Line-Oriented Flight Training) scenarios are included. At the end of the course, a Check Airman carries out a formal check. He is authorised by the Thai Department of Aviation (DOA).
It is not a requirement, but all pilots, not including 'cruise pilots', train with experienced aircraft instructors in the aircraft itself.
After Transition Training, pilots fly with flight instructors on the line for about 2–4 months. This helps pilots to get Initial Operating Experience (IOE).
However, if the Transition Training is included in the Promotion Training program, a pilot must pass more check rides before he can be released for unrestricted line flying.
The Transition Training time varies with aircraft type, and depends on the complexity of the aircraft and its equipment.
During the Transition Training course, pilots learn to operate specific aircraft under normal, abnormal, and emergency conditions. The course also includes a comprehensive technical section. This covers aircraft systems, performance, and operating procedures.
Full and advanced Flight Simulators are used in the last part of the training. This covers normal, abnormal, and emergency situations in-flight and on the ground. Realistic LOFT (Line-Oriented Flight Training) scenarios are included. At the end of the course, a Check Airman carries out a formal check. He is authorised by the Thai Department of Aviation (DOA).
It is not a requirement, but all pilots, not including 'cruise pilots', train with experienced aircraft instructors in the aircraft itself.
After Transition Training, pilots fly with flight instructors on the line for about 2–4 months. This helps pilots to get Initial Operating Experience (IOE).
However, if the Transition Training is included in the Promotion Training program, a pilot must pass more check rides before he can be released for unrestricted line flying.
RECURRENT TRAINING

Every 6 months, all THAI pilots must do a Recurrent Flight Training program. This program consists of:
1. A review of operational experiences, and a review of the pilot's technical knowledge and emergency procedures.
2. Review and training for aircraft handling proficiency using a Full Flight Simulator. This session covers areas not usually encountered during line operations and consists mostly of out-of-the-ordinary procedures.
3. A CRM LOFT (Line-Oriented Flight Training) session in the Full Flight Simulator. This session is planned in detail, using the principles of CRM (Crew Resource Management).
The objective of this session is to give pilots real experience and training in a realistic scenario. The pilots, as a team, must control stressful situations, and solve problems that come from many directions and sources. The main objective to be practised in this skill, team, and management process is the safety of the flight and its passengers.
Every THAI pilot must successfully pass the Recurrent Flight Training program every 6 months in order to continue flying THAI aircraft on THAI routes.
1. A review of operational experiences, and a review of the pilot's technical knowledge and emergency procedures.
2. Review and training for aircraft handling proficiency using a Full Flight Simulator. This session covers areas not usually encountered during line operations and consists mostly of out-of-the-ordinary procedures.
3. A CRM LOFT (Line-Oriented Flight Training) session in the Full Flight Simulator. This session is planned in detail, using the principles of CRM (Crew Resource Management).
The objective of this session is to give pilots real experience and training in a realistic scenario. The pilots, as a team, must control stressful situations, and solve problems that come from many directions and sources. The main objective to be practised in this skill, team, and management process is the safety of the flight and its passengers.
Every THAI pilot must successfully pass the Recurrent Flight Training program every 6 months in order to continue flying THAI aircraft on THAI routes.
OTHER TRAINING
For pilots, training is a never-ending task. It consists of more than the normal training areas described above.
Every airline introduces new training courses for its pilots when new trends start, new techniques and equipment are introduced, and special events happen in the airline industry. For example, when THAI aircraft started using RVSM (Reduced Vertical Separation Minima) and EGPWS (Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning System), additional pilot training was essential. Other examples are Flight Instructor Courses, Supervisory Pilot Courses, and Quality Management Courses for pilot managers in the Flight Operations Department.
All these training courses, all these efforts to increase awareness and quality, are based on one important principle: Safety and quality must come first. To reach that goal, training is a critical and essential tool.
Every airline introduces new training courses for its pilots when new trends start, new techniques and equipment are introduced, and special events happen in the airline industry. For example, when THAI aircraft started using RVSM (Reduced Vertical Separation Minima) and EGPWS (Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning System), additional pilot training was essential. Other examples are Flight Instructor Courses, Supervisory Pilot Courses, and Quality Management Courses for pilot managers in the Flight Operations Department.
All these training courses, all these efforts to increase awareness and quality, are based on one important principle: Safety and quality must come first. To reach that goal, training is a critical and essential tool.















































